C2 Tracking Approaches: From Search Engines to Managed Feeds
Aug 21, 2025
Command and Control (C2) infrastructure tracking is a cornerstone of modern cyber threat intelligence (CTI). By identifying and monitoring attacker-controlled servers, defenders can block malicious communications, detect intrusions earlier, and ultimately reduce the dwell time of threats within their environments.
With so many platforms and techniques available, each offering unique strengths, how can CTI teams, MSSPs, and SOCs determine which tools are best suited to their needs?
This article lists some of the leading C2 tracking approaches, providing insights on methodology, update frequency, data format, and integration support, helping defenders build a practical, layered visibility stack.
Why C2 Tracking Matters
C2 infrastructure forms the backbone of attacker operations. It is used to:
- Control compromised endpoints
- Deliver second-stage payloads
- Exfiltrate stolen data
- Manage botnets or implants
Interrupting C2 communications, particularly early in the kill chain, can help prevent large-scale damage and stop threats before they escalate.
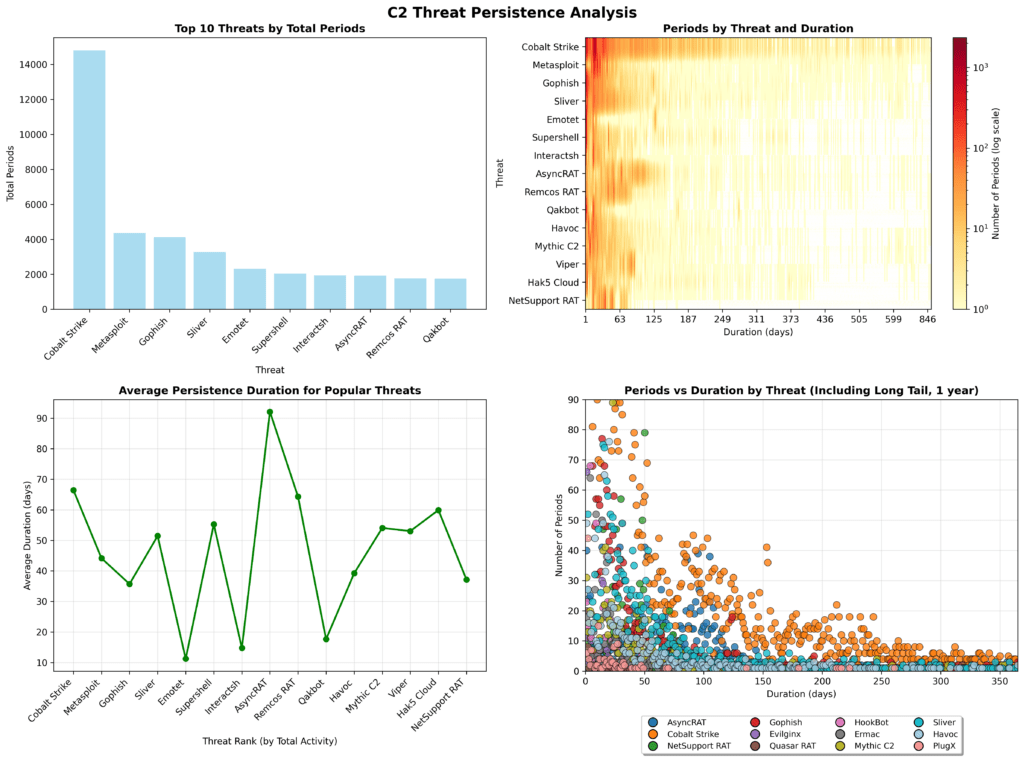
C2 servers display a range of persistence durations. Although they are inherently short-lived, some servers remain active for extended periods. While the average lifespan of many popular threats is around 50 days before mass detection or takedown, there is significant variation. Thousands of cases have lifespans of just 1 to 5 days. Others, like Havoc C2, persist up to approximately 10 days or more, and outliers, including some instances of AsyncRAT, exceed 900 days. The increasing speed of detection drives threat actors to automate provisioning new infrastructure, responsible for these short-lived instances, often replicating similar configurations or procedural patterns. For long-lived servers, advanced obfuscation or infrequent updates may contribute to their durability. Deployment is frequently accelerated by modular C2 frameworks like Sliver or Mythic C2, while the dominance of top threats, with Cobalt Strike accounting for over 14,000 periods, highlights their widespread adaptability in the current threat landscape.

C2 Tracking Techniques
Modern C2 trackers rely on a mix of passive and active scanning, pivoting, machine learning, and heuristic detection to uncover malicious infrastructure. Some of the most effective signals include:
- TLS/SSL Certificates
- HTML Title, Headers
- HTML Content
- SSH Keys
- Domain Patterns, WHOIS data
- JARM Hashes
- JA4 Fingerprints
- TCP Banners
- Favicon hashes
✅ Top 10 C2 Tracking Tools
| Tool | Key Strengths |
| Shodan | Huge dataset from internet-wide scanning, feature to rescan popular ports, quick detection through real-time querying and specialised tools like Malware Hunter, which actively identifies C2 servers by simulating infected devices and sending handshakes to IPs |
| Censys | Good port scanning range and freshness of the results from regular updates, recent changes and syntax revamp made many old searchers not working; provides historical fingerprints and data for tracking infrastructure changes over time, enabling identification of C2 servers even before active use |
| Fofa | Sometimes you find things other resources may not show due to its unique indexing and coverage, good historical data for long-term tracking; comparable to other engines in port and device scanning but excels in uncovering niche or regionally specific C2 artifacts |
| Netlas | Embraces automation, scans domains, not just IP, which allows to detect threats hidden behind CDNs, data is consistent for each host, no need to check when a particular port was rescanned; supports proactive threat hunting for C2 components with discreet, detailed insights into attack surfaces |
| Hunt.io | Deep specialisation in malicious infrastructure with great C2 Detection, quick detection and rescan of known malicious infrastructure, including opendir analysis |
| Validin | Excellent domain pivoting; helps follow C2 infrastructure as attackers rotate domains by correlating DNS data and historical records; enhances detection through monitoring unusual patterns in domain resolutions and callback mechanisms common in C2 setups |
| Criminal IP | Not only gives raw data but also threat context and scoring, Good Domain Search feature for pivoting on C2-related domains |
| ZoomEye | Good port coverage across devices, quick results from efficient indexing, popular ports updated very often while some non-standard may be out of priority; strong for rapid scanning and comparison in threat hunting scenarios alongside similar tools |
| UrlScan | Not only it is great for phishing, also can help to identify HTTP based C2 through URL analysis for suspicious connections and malicious redirects; good way to visually see the C2 panels via screenshots and behavioural insights |
| RST Cloud | Advanced IOC scoring and malware mapping. Effortless access to C2 data that is still green on VirusTotal, with scoring to filter out noisy results when a C2 is hosted on an IP that hosts multiple domains (e.g., Cloudflare). Teams that need actionable results and lack time for tracking C2 and cleaning data for operationalisation. |
By combining various tracking techniques with internet scanning and search engines, you can identify malicious C2 infrastructure in near real time. This involves detecting patterns or anomalies in server responses, SSL certificates, HTTP headers, domain names, and other parameters that distinguish malicious infrastructure from legitimate systems. Some tracking techniques using RST Cloud and Netlas.io solutions are described here: Tracking Techniques Walkthroughs.
A lot of C2 search query examples and search results are available online and shared in public repositories. We would refer to the free repositories like Montysecurity C2 Tracker, ThreatFox, and Viriback C2 Tracker.
For detailed examples of tracking techniques, please refer to these resources:
- Tycoon2FA: Invisible Unicode Characters Task Research (RST Cloud Youtube channel)
- C2 Tracker: How to perform effective C2 Hunting (Hunt.io blog)
C2 tracking is a constantly evolving discipline. To maintain an advantage, organisations should focus on people’s skills that will allow to choose the right tools that provide frequent, real-time updates, enable enrichment and context-based attribution, and minimise false positives through effective scoring and contextualisation.
Want help evaluating RST C2 Tracker? Let’s talk.